
Germain Racing is an American professional stock car racing team that exclusively competes in the Monster Energy NASCAR Cup Series. The team races the No. 13 GEICO Chevrolet Camaro ZL1 and is currently upgrading its cars to meet the new 2019 NASCAR design requirements.
Stock car racing is an exciting field, inspiring many especially with the fraternity of mechanical engineers and racers taking part in competitions around the globe. In modern racing, many advanced technologies are available, and it is therefore imperative to be up-to-date to keep a competitive edge. In race car dynamics, even a small design change can shave off seconds that matter in a race. With the new aerodynamic package released by NASCAR for next year, more design changes than ever will be needed for racers to compete and comply with racing regulations.
Germain Racing is using the SimScale cloud-based simulation platform to optimize their car design and reduce drag for higher speed.
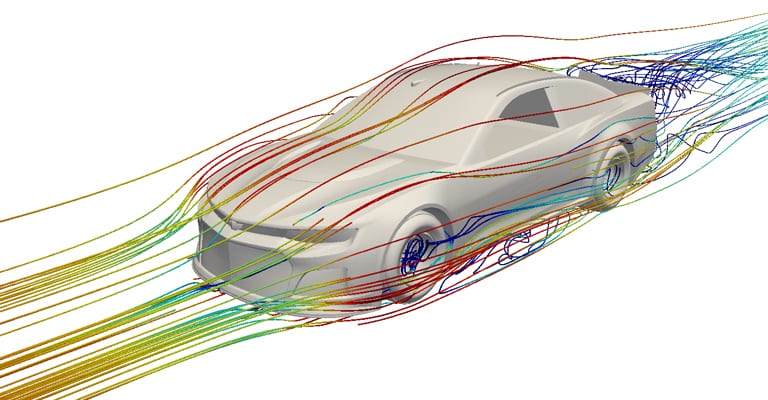
This is done by computing and observing the airflow as it moves. SimScale can also provide the drag of each car design or of individual components, which helps designers track their progress with every design improvement.
Airflow and pressure distribution around the car determined with SimScale are used to compare designs both qualitatively and quantitatively.
SimScale is very quick and easy to use. It gives us a relatively low-cost way of examining the car’s behavior, with very little wind tunnel time. Onshape allows us to make surface changes very quickly, and import our native CAD files directly to SimScale.
Matt Borland
Crew Chief at Germain Racing
The model was created in the cloud using Onshape, directly supported from the SimScale interface. A highly optimized mesh was generated to capture the turbulent airflow around the vehicle. The final mesh had around 28 million cells.
Each simulation was run on a 96-core machine and typically for less than 7 hours.
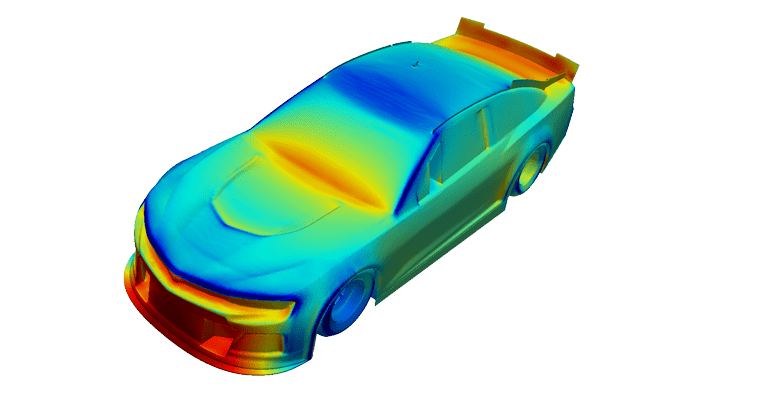
It was possible to perform multiple simulation runs in parallel, with different incident angles to mimic the car driving around a curve. Hence, the same vehicle speed was defined in multiple directions, which is typical for analyzing race car dynamics. This means that within a single working day, multiple results can be analyzed and design decisions can be made.
It was noticed that small vortices were formed in different local regions around the vehicle with different designs. There were also large recirculation areas behind and under the car.
Very high drag was noticed on the rear spoiler/vertical wing and also on the closed grill in front of the vehicle. Additionally, an interesting discovery made by SimScale predicted higher drag in certain sections of the wheels when they were angled in different directions. This gave a good indication of how the design could be optimized and where focus was required.

SimScale was used to understand how the car was producing downforce and to optimise this while simultaneously reducing the overall drag. The end-to-end workflow from CAD to airflow to even drag results, went from being months to just a single day using SimScale for simulation instead of traditional, desktop-based CAE software.
SimScale predicted higher drag in certain sections of the wheels when they were angled in different directions. This gave a good indication of how the design could be optimized and where focus was required.




Sign up for SimScale
and start simulating now