Coolrite is a specialist refrigeration and air conditioning design and services firm. Innovation has always been a key driver of the company and they have consistently led change within the Irish market and continually strive to be the best. Coolrite uses the latest technology available to deliver the most energy-efficient refrigeration and air conditioning systems to their customers. Coolrite designs, sells, installs, and services refrigeration systems. With 18 vehicles and 42 full-time staff, they have all of the resources and knowledge within the organization to cater to any and all refrigeration requirements and cold supply chain requirements.
Coolrite products use the latest technological advances so that they have the highest energy ratings available on the market and are installed to ensure that annual energy running costs are minimized. The critical design services Coolrite offers are for the following:
Gerard Lally is the Technical Sales Manager at Coolrite and a SimScale user. His team uses 3D models created in various file formats to upload directly into SimScale and begin simulations. The fact that SimScale can import multiple file types is a big advantage as they receive models from numerous subcontractors working on behalf of clients including pharmaceutical companies, food processing plants, and supermarkets.
The key insights Gerard and his team are looking for inside their refrigerated chambers include:
In various industries such as pharmaceuticals, food storage, and scientific research, maintaining precise temperature conditions within refrigerated spaces is critical to preserving the quality and integrity of stored materials. The advent of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) has revolutionized the way engineers and scientists analyze and optimize temperature distribution within these controlled environments. In this article, we delve into the application of CFD to simulate temperature distribution inside a refrigerated cold room with a cooling plant, using a real-world example of a pharma plant’s cold storage facility.
CFD is a branch of fluid mechanics that uses numerical analysis and algorithms to solve and simulate the behavior of fluid flows and heat transfer processes. CFD allows engineers to visualize complex fluid flow patterns, temperature distribution, and other related phenomena within a given environment. In the context of a refrigerated cold room, CFD enables us to accurately predict temperature variations, identify potential hotspots, and optimize the cooling system’s performance.
Consider a refrigerated chamber that requires a cold room to store raw materials within a temperature range of 2° C to 8° C. Deviations from this temperature range could lead to spoilage and economic losses. The cold room is equipped with a cooling plant having a duty-standby configuration and a cooling capacity of 4.5 kW. The cooling plant’s demand is influenced by factors like air ingress due to door openings and ambient conditions. The challenge is to ensure a uniform temperature distribution throughout the cold room while accounting for these dynamic variables.
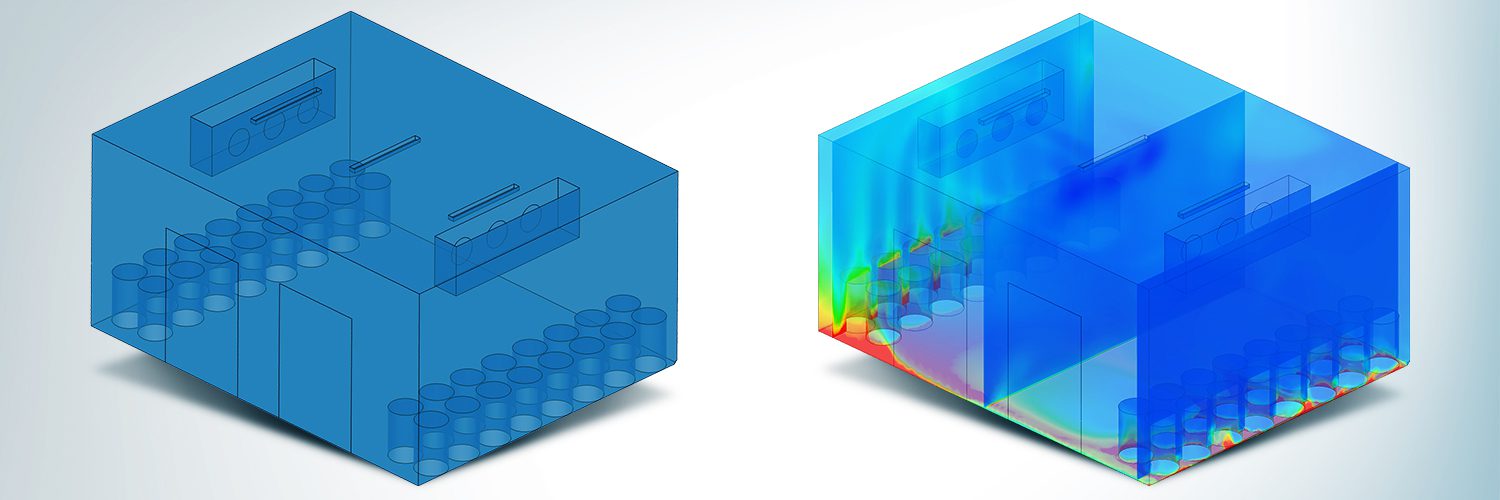
To simulate temperature distribution, a virtual 3D model of the cold room and its contents is constructed in CAD software and imported into the CFD platform, SimScale. The model includes the cold room’s dimensions, insulation properties, door location, and the cooling plant’s specifications. The raw materials are virtually represented within the model, and their thermal properties are defined.
Various boundary conditions are applied to replicate real-world scenarios. These conditions encompass the initial temperature distribution, cooling plant operation, door-opening events, and external ambient temperature changes. For instance, when the door is open, CFD simulates an influx of warm air, affecting the heat balance of the room and hence, temperature.
CFD software employs numerical solvers to model the governing equations of fluid flow and heat transfer. The Navier-Stokes equations, which describe fluid motion, and the heat transfer equations, which govern temperature changes, are numerically solved over the computational grid representing the refrigerated chamber. These simulations analyze the heat transfer mechanisms, including conduction, convection, and radiation, as well as fundamental fluid behavior such as compressibility and turbulence. Consequently, CFD provides crucial insights into the behavior of moving fluids, offering data on parameters like velocity, temperature, and pressure. The simulations track fluid flow patterns, temperature changes, and heat exchange rates within the cold room.
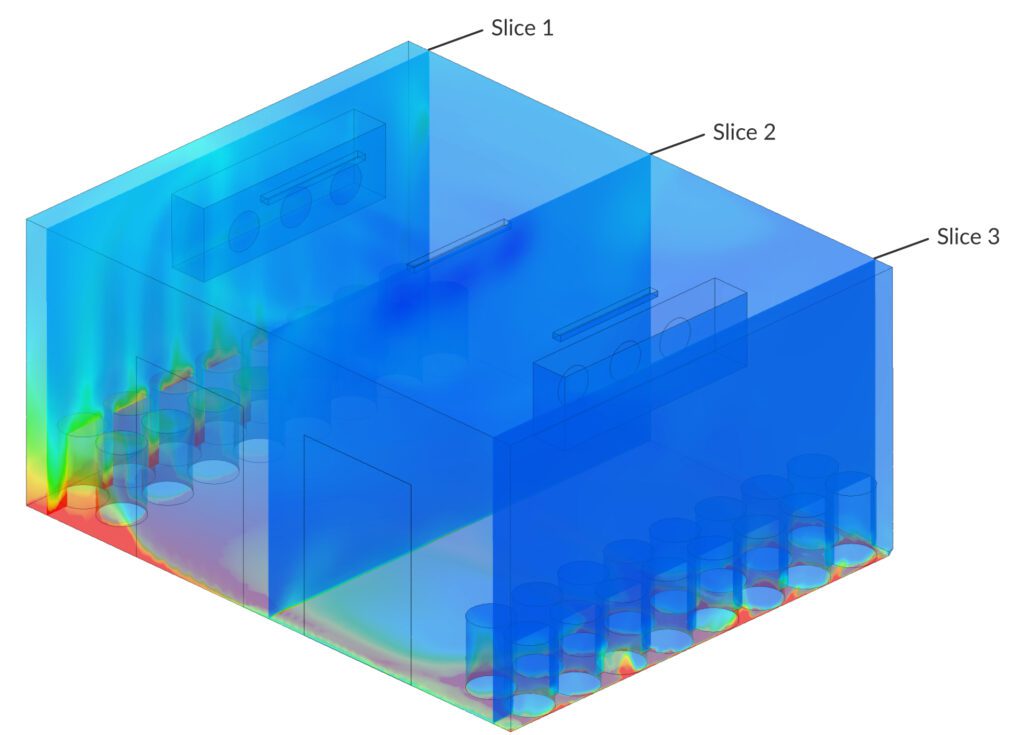
Using SimScale, Coolrite can set up and run multiple design conditions in parallel by making minor adjustments to either the CAD model (e.g., floor area, volume, and placement of ventilation openings), the simulation parameters (e.g., boundary conditions, flow rates, ambient conditions), or both. The simulation generates temperature profiles that visually represent the temperature distribution within the cold room. These profiles indicate areas where temperatures might exceed the specified range, helping engineers identify potential hotspots.
CFD simulations allow for sensitivity analysis, where engineers can assess how changes in variables impact temperature distribution. For example, the impact of longer door openings on temperature variation can be evaluated, aiding in the optimization of door usage protocols.
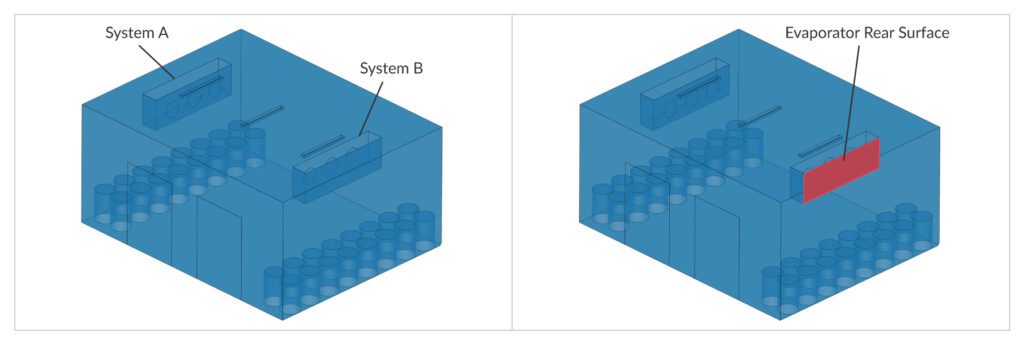
By analyzing simulation data, engineers can fine-tune the cooling plant’s operation strategy. This might involve adjusting cooling plant duty cycles, optimizing standby mode transitions, or even suggesting physical changes like adding air curtains near the door to minimize temperature disturbances during door openings.
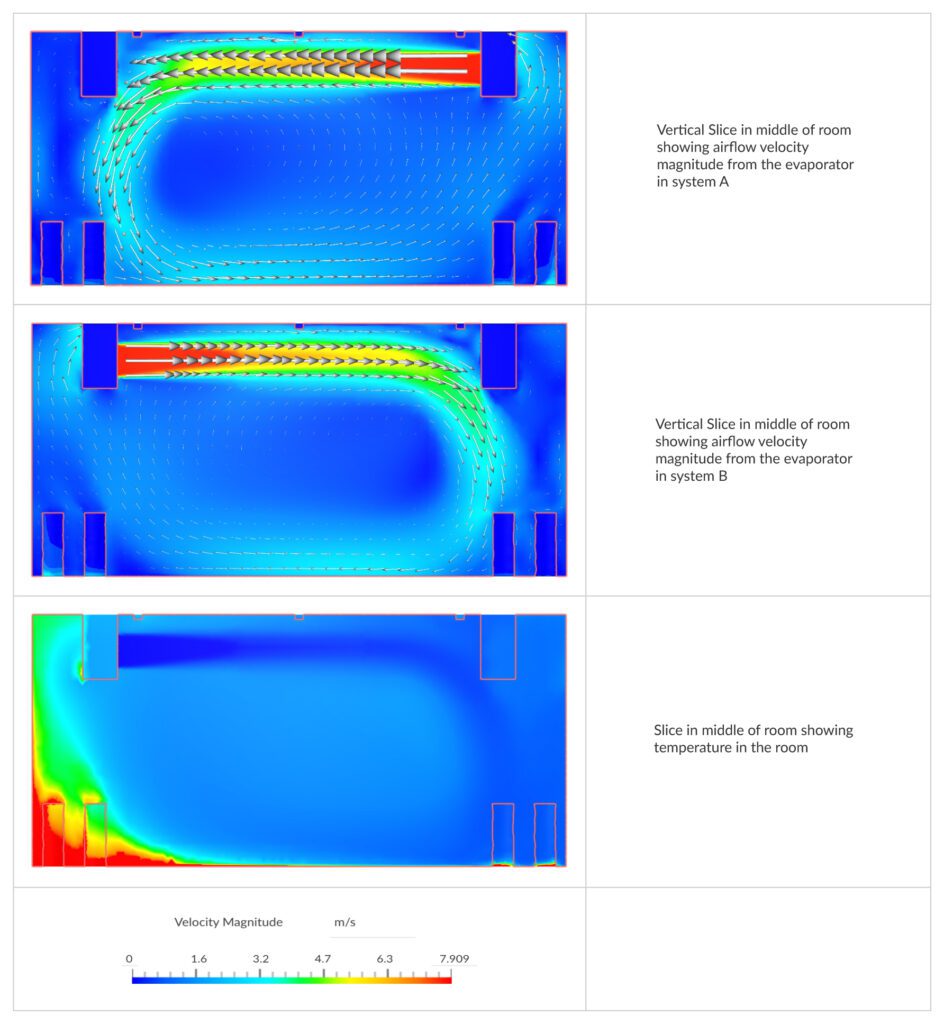
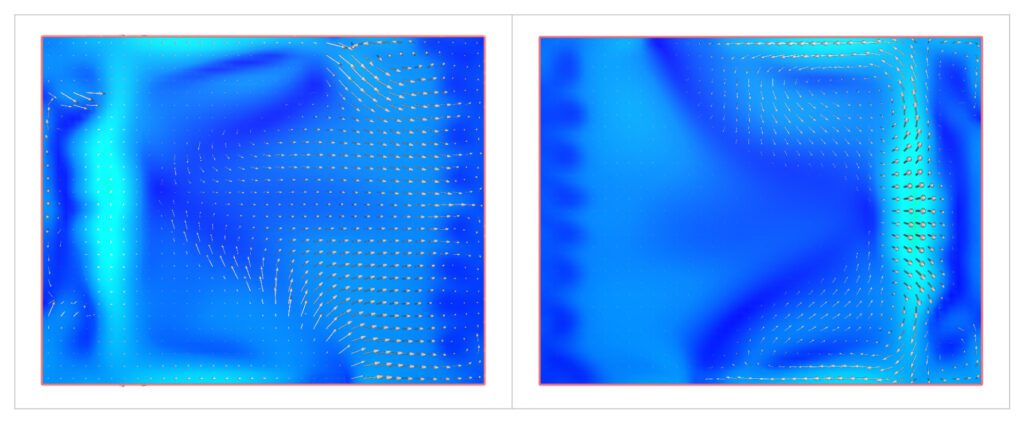
Using Computational Fluid Dynamics to simulate temperature distribution within a refrigerated cold room offers invaluable insights into maintaining a controlled environment for storing sensitive materials. The case study of a refrigerated cold storage facility demonstrates how CFD aids in visualizing temperature patterns, optimizing cooling plant operations, and ensuring compliance with temperature requirements. As CFD techniques continue to advance, industries reliant on temperature-sensitive storage can expect improved efficiency, reduced losses, and enhanced product quality through informed decision-making.
The customer support from SimScale is great and helped to reduce the learning curve when we first started with SimScale. We used to outsource CFD modeling to a third-party consultant. The annual license for SimScale costs less than getting a subcontractor to issue just one report so the return on investment (ROI) for us is just a few months and it has given us the freedom to explore more design options.

Gerard Lally
Technical Sales Manager at Coolrite

Sign up for SimScale
and start simulating now