Heat dissipation is one of the deciding factors in designing heat transfer components. For example, we can use the heat dissipation capabilities to determine the effectiveness of a heat exchanger.
Using CFD, how can we calculate the amount of heat dissipated from a fluid?
Solution
To determine how much heat a fluid loses (or gains) through a system, we can use the following equation:
$$ Q = m C_p \Delta T \tag{1} $$
Where \(Q\) (\(W\)) is the heat that the fluid loses/gains, \(m\) (\(\frac{kg}{s}\)) is the mass flow rate of the fluid, \(C_p\) (\(\frac{J}{kg.K}\)) is the specific heat of the fluid, and \(\Delta T\) \((K)\) is the temperature difference between the outlet and the inlet.
In the next section, we will show how to use this formula, using a heat exchanger as an example.
Expected Outcome
Let’s consider a Conjugate heat transfer (CHT v2.0) simulation using the shell and tube heat exchanger from Figure 1:
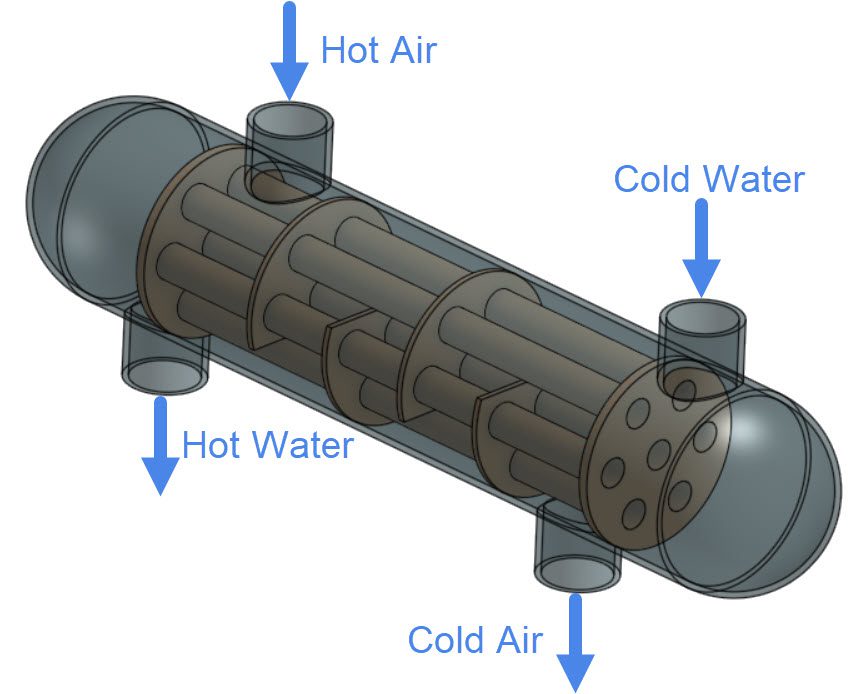
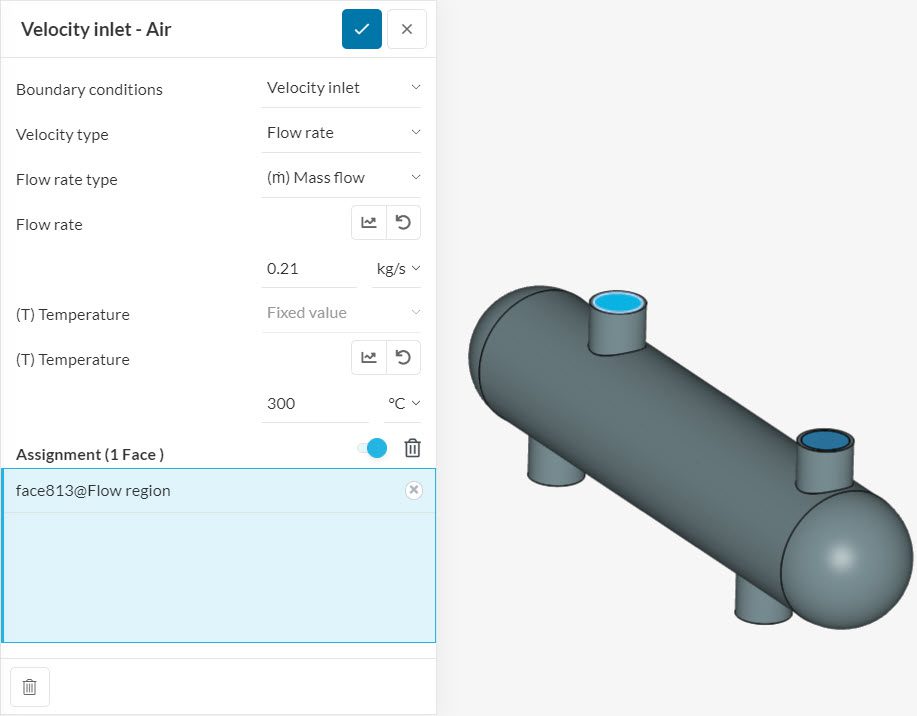
From equation 1, we know what information is necessary to calculate the heat dissipation on the hot fluid. The total air mass flow rate \(m\) and the inlet air temperature \(T_{Inlet}\) are provided as a boundary condition for the simulation.
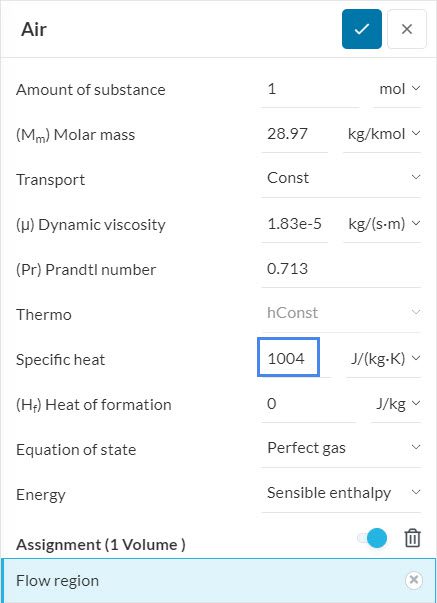
Under the Materials tab, we can obtain the specific heat \(C_p\) of the fluid:
Before calculating the amount of heat that dissipates from the hot air, we need to determine the air outlet temperature. To obtain this information, we can set an Area average result control for the air outlet, and run the CHT v2.0 simulation.
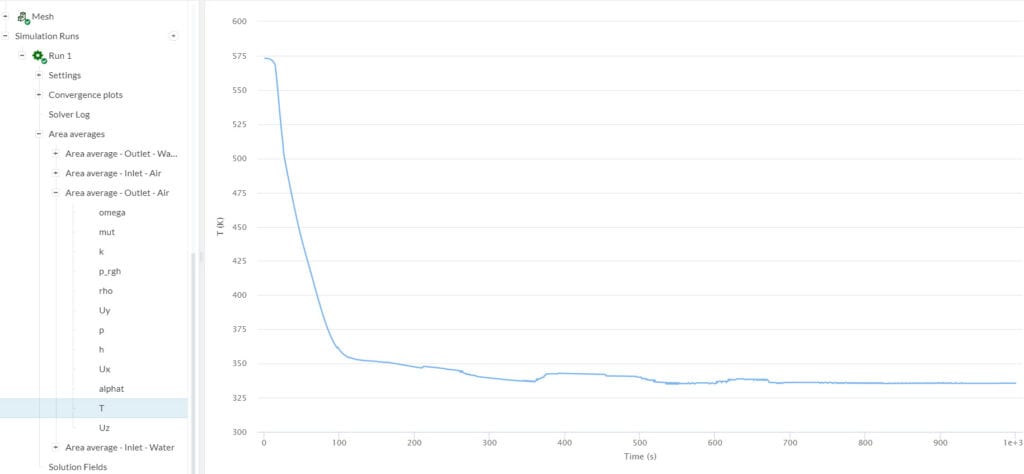
Using equation 1 as a reference, the total heat dissipated (\(Q\)) from the hot air in this example is:
$$ Q = 0.21 \times 1004 \times (335.58\ – 573.15) =\ – 50089\ W \tag{2}$$
Note that the value of \(Q\) in equation 2 is negative since the hot air loses heat through the system.
If you would like to learn more about heat exchangers, please check out this step-by-step tutorial.
Note
If none of the above suggestions solved your problem, then please post the issue on our forum or contact us.
