Today, desktop-based and on-premises computer-aided engineering (CAE), or more specifically, CAE simulation software, still remains to have the largest hold on the market for each respective facet of engineering. This can be credited to its 30+ years of development, allowing this kind of software to adapt and offer features that boast high accuracy for specific and niche applications.
However, cloud-based CAE software is taking more and more market share as globalization, higher competition, and agile working environments increase in parallel. In this blog, we will take a comparative look at both types of CAE software, and what this could mean moving forward for engineers.

On-Premises CAE Software
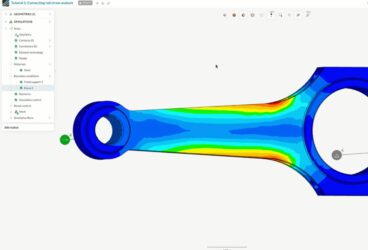
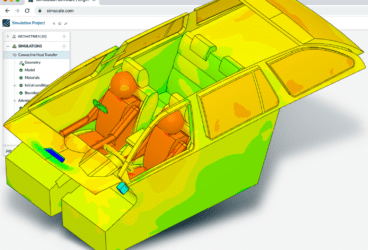
So what do we mean by on-premises CAE software? Essentially, this refers to all simulation software that supports and enables engineering analysis tasks from a stationary workplace, i.e. desktop computer. CAE software can encompass everything from finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), multibody dynamics (MDB), and thermodynamics to include further optimization capabilities and features. CAE software enables engineers to simulate, validate, and optimize products and manufacturing tools. The top CAE software solutions, including on-premises and cloud-based as announced by g2.com, include MATLAB, Fusion 360 Simulink, NI Multisim, SimScale, Abaqus, Solid Edge, etc., in no particular order.
Industry-standard CAE software solutions run using on-premises infrastructure. Without a background in engineering simulation or supporting IT infrastructure/staff, this setup can prove to be troublesome. Digging deeper, there are high fixed costs for purchasing hardware that is required for an on-premises tool. Secondly, maintenance, hardware upgrades, and energy consumption need to be considered. Lastly, this forces users into a specific setup—it is not easy to adapt resources to changing demands, with often even software licenses being dependent on cluster size. On-premises CAE software historically also has a steep learning curve before employees are able to run simulations and ensure maintenance and data management.
On-premises software refers solely to the programs that need to be installed on local hardware and devices for engineering and consulting businesses. In these cases, the stakeholder or team will typically purchase a licensing module that shares the purchased license credits to the most active users, including a maximum limit of parallel jobs, and unfortunately sometimes creating a bottleneck at peak times that can slow overall time-to-delivery.

While these types of software boast optimized user-friendliness and simulation workflow, this customarily comes at a price; costs for commercial CAE packages can range from $10,000 to $50,000+ per workstation. Extending your simulation capabilities to utilize a larger amount of cores will further increase the budget required, making the turnaround time more expensive.
Cloud-based CAE, on the other hand, can be run by professionals in every facet of industry without a background in HPC systems or engineering simulation, has more flexible pricing structures, allows an infinite number of parallel jobs eliminating workflow jams, and was created to ultimately optimize what on-premises software has been doing for decades before. SaaS solutions fill this growing untapped potential for on-demand engineering simulation capabilities by leveraging the performance and scalability of HPC systems in the cloud and eliminating high upfront costs and other outdated pricing models.
This paper addresses the difference between on-premises software and SaaS
solutions for computer-aided engineering, explaining how SaaS came to be and its
key benefits.
What Is SaaS?
Software as a Service, also known as SaaS, is a cloud-based service where instead of downloading and installing software from your desktop PC or business network to run and update manually, you alternatively enter an application via an Internet browser.
The subscription-based software application could be anything from office software to unified communications among a wide range of other business apps that are available, as well as CAE. SaaS has essentially changed the landscape for software, through harnessing the power of the Cloud. Yet, that’s not to say it doesn’t come without some drawbacks. The largest issue users can note about SaaS products is that they require an Internet connection to operate. Of course, without the Internet, one cannot run a simulation on the cloud, while in an airplane (in the clouds).

However, the increasingly wide availability of broadband and high-speed phone networks such as 5G makes this less of an issue. Today, there is almost nowhere you can go that does not offer WiFi or some rendition of Internet access. Additionally, some SaaS applications have combatted this issue by offering offline modes that allow basic functionality, for example, Google Docs.
Benefits of SaaS Tools
Key benefits of SaaS cover accessibility, compatibility, and operational management. SaaS models allow lower upfront investments than traditional software download and installation, making them more affordable and by proxy available to a wider range of individual users and businesses alike, making it easier for smaller companies to disrupt existing markets.
The most commonly cited benefit of SaaS products is accessibility. All SaaS applications can be run via a web browser, regardless of the operating system. This brings a level of versatility never before seen in standard desktop-based software, as not only does it mean users of Mac, Windows, and Linux operating systems can coexist on the same cloud-based platform, but it allows users to access their data across different devices, whether it be a desktop PC, laptop, tablet, or combination. Let’s look at some other key advantage areas.

Updates and maintenance: Another major advantage of SaaS is that because they run in the cloud, the provider can update its software centrally without negatively affecting business operations for its users. This is an innate difference to desktop-based or on-premise CAE simulation software that will often require a degree of compatibility and endpoint security.
Data and analytics: Companies using SaaS products normally have access to reporting and intelligence tools and visualizations that can give invaluable insights into operations, allowing workflow streamlining and optimization. Since access depends on a paid subscription, vendors can sleep soundly with no concerns about piracy which might otherwise cost the supplier, thereby damaging both access and pricing models.
Saving and storage: On-premise storage of data requires heavy investment in reliable backups such as through online cloud storage in order to mitigate hardware crashes that might otherwise cause a significant loss of data. SaaS, on the other hand, routinely saves data in the cloud automatically. Through the cloud, employees from all over the globe can access information, as well as switch between devices without losing work or data, by logging into a single account, regardless of which device is being used. With CAE simulation software specifically, this saves a lot of headaches.
Market reach: For the providers of SaaS, this refers to being able to supply a software service to the majority of the respective market, instead of just a limited and targeted market segment. Pricing plans can be offered at cheaper prices, and make software options more accessible to businesses of every size. For users this implies being able to reach services not commonly available, thus both expanding and enhancing business services, productivity, and endless opportunities.
SaaS and CAE Simulation
Now that you are familiar with the key similarities and differences between on-premises and SaaS, it is helpful to keep this six-point checklist in mind when considering CAE, and more specifically CAE simulation tools.
- What is the cost of hardware needed?
- What will the annual renewal costs be?
- What training time is required to learn the tool?
- What time is required to see and track project statuses?
- What is the opportunity cost of working sequentially versus in parallel?
- Will the tool be difficult to scale?
Using this checklist, you can easily compare the benefits of different types of software in-line with the needs of your engineering team, to ultimately choose the most efficient and cost-effective CAE software solution for you!
Interested in learning more about how cloud-based CAE simulation could increase your team’s time-to-delivery and optimize your iterative design process? Check out some of these recent blog articles:
- 3 Things to Consider as Your Engineering Team Grows
- Simulation in the Cloud: Tips for a Seamless Migration
- 3 Places Where Your Design Process Is Slowing Your Time to Delivery
- Cloud Migration in 2020: The New Digital Workplace